12,400 sf Industrial Sublease
Description
Available at the building is a 12,400 sf fenced-off section of the ground floor warehouse. The space features 19’ ceiling height, up to 5 car rooftop parking, 3 trailer-deep loading docks and 1 drive-up ramp into the building. Loading is shared with the master tenant, although their operation is largely during off-peak hours.
Centrally located in Long Island City, less than a mile to the entrance ramp to the Long Island Expressway and the 7 subway line. Ideal for a wide variety of industrial users.
Documents
Location
Sq Ft
Financials
Construction
Image Gallery

Area Profile
Western Queens (LIC, Astoria, Maspeth, Woodside)
The Western Queens area, including neighborhoods like Long Island City, Maspeth, Astoria, & Woodside, has long been a significant industrial hub in Queens, known for its mix of manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution centers as well as its proximity to Manhattan. Despite residential rezoning along the waterfronts in Long Island City and Astoria, Western Queens still retains a substantial industrial presence and has further evolved into a major hub for the film and television industry.
Maspeth in particular has remained a predominantly industrial area. As the geographic center of New York City, is a strategic location for logistics, distribution and warehousing as well as heavy manufacturing.
Proximity to Major Highways: Strategically located near major highways such as the Long Island Expressway (I-495), Brooklyn-Queens Expressway (I-278), and Grand Central Parkway.
Access to Bridges and Tunnels: Convenient access to several key bridges and tunnels, including the Queensboro Bridge (59th Street Bridge), Triborough Bridge (Robert F. Kennedy Bridge), and Queens-Midtown Tunnel.
Public Transportation Hubs: Served by multiple subway lines (such as the 7, N, W, E, M, R) and bus routes, providing residents and workers with extensive public transportation options.
Proximity to Airports: Close to LaGuardia Airport, one of New York City's major airports, facilitating convenient access for businesses involved in logistics and transportation.
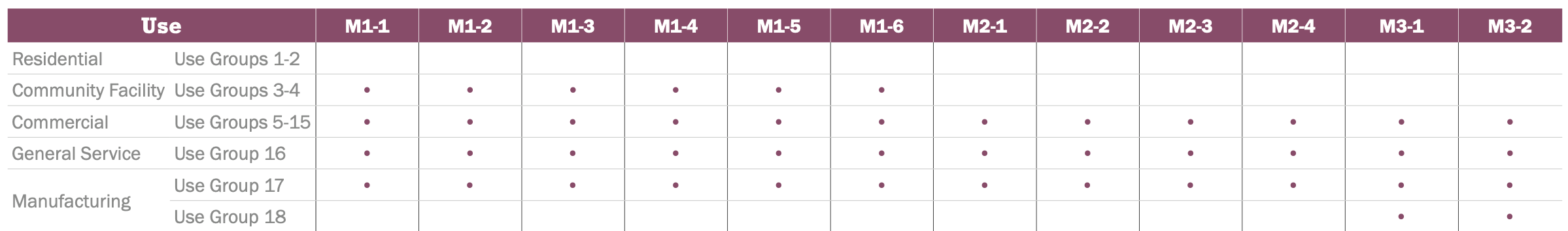
Zoning
M3-1 Zone
M-zones are designed to accommodate a variety of industrial and manufacturing activities, including heavy and light manufacturing, warehousing, distribution centers, and storage facilities. These areas are regulated by zoning laws to ensure compatibility with surrounding neighborhoods and to manage issues such as noise, traffic, and environmental impacts.
Typical Uses
Typical uses include power plants, bulk storage, recycling and waste management, heavy repair, construction facilities, concrete plants, etc.